Technical analysis (TA) is a powerful tool used in crypto trading to forecast future price movements based on historical price data, trading volume, and market behavior. Unlike fundamental analysis, which evaluates a project’s intrinsic value, technical analysis focuses purely on price charts, patterns, and indicators.
In this guide, you will learn how to conduct deep technical analysis for cryptocurrencies, identify trends, use indicators, and build a strong trading strategy.
1. Basics of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is built on three main principles:
- Market Discounts Everything – All known information is reflected in the price.
- Price Moves in Trends – Prices follow trends rather than moving randomly.
- History Repeats Itself – Market patterns repeat due to trader psychology.
1.1 Types of Charts Used in Crypto TA
- Line Chart – Simple representation of price movement over time.
- Bar Chart – Displays opening, closing, high, and low prices per time interval.
- Candlestick Chart (most used) – Shows price movement with detailed visualization.
Each candlestick has four components:
- Open Price – The price at the beginning of a time frame.
- Close Price – The price at the end of the time frame.
- High Price – The highest price reached.
- Low Price – The lowest price reached.
2. Identifying Market Trends
A trend is the general direction of a crypto asset’s price movement over a period of time.
2.1 Types of Market Trends
- Uptrend (Bullish) – A series of higher highs and higher lows.
- Downtrend (Bearish) – A series of lower highs and lower lows.
- Sideways (Range-Bound) – When price consolidates within a horizontal range.
2.2 Trendlines
A trendline connects key price levels and helps to define the trend:
- Uptrend Line – Drawn along rising lows.
- Downtrend Line – Drawn along falling highs.
2.3 Support & Resistance
- Support – A price level where demand is strong enough to prevent further decline.
- Resistance – A price level where selling pressure prevents further rise.
Once broken, support can turn into resistance, and resistance can turn into support.
3. Key Technical Indicators
Technical indicators help confirm trends and generate trade signals.
3.1 Moving Averages (MA)
MAs smooth out price action to identify trends:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA) – The average price over a set period.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA) – Similar to SMA but gives more weight to recent prices.
Common settings:
- Short-term: 9, 21-day MAs (used for quick trades).
- Medium-term: 50-day MA (used for trend confirmation).
- Long-term: 200-day MA (used for major trend reversals).
Golden Cross – When a short-term MA crosses above a long-term MA (bullish signal).
Death Cross – When a short-term MA crosses below a long-term MA (bearish signal).
3.2 Relative Strength Index (RSI)
RSI measures momentum on a scale of 0 to 100.
- Above 70 – Overbought (price may correct).
- Below 30 – Oversold (price may rebound).
Divergences:
- Bullish Divergence – Price makes lower lows, but RSI makes higher lows → Possible reversal upward.
- Bearish Divergence – Price makes higher highs, but RSI makes lower highs → Possible reversal downward.
3.3 MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
MACD consists of:
- MACD Line (fast-moving line).
- Signal Line (slow-moving line).
- Histogram (difference between MACD and Signal line).
When MACD crosses above the Signal line → Buy Signal
When MACD crosses below the Signal line → Sell Signal
3.4 Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands consist of:
- Middle Band (SMA)
- Upper Band (+2 Standard Deviations)
- Lower Band (-2 Standard Deviations)
When price touches upper band → Overbought (potential reversal).
When price touches lower band → Oversold (potential bounce).
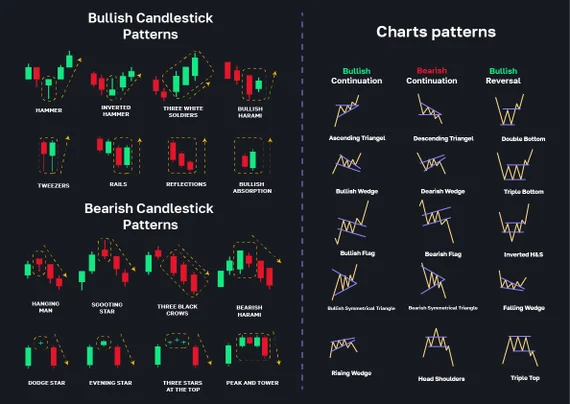
4. Chart Patterns & Candlestick Formations
Patterns help traders anticipate price movements based on historical behavior.
4.1 Common Chart Patterns
- Ascending Triangle – Bullish breakout pattern.
- Descending Triangle – Bearish breakdown pattern.
- Head and Shoulders – Bearish reversal pattern.
- Inverse Head and Shoulders – Bullish reversal pattern.
- Double Top – Bearish pattern indicating a strong resistance.
- Double Bottom – Bullish pattern indicating strong support.
4.2 Candlestick Patterns
- Bullish Engulfing – A strong bullish reversal signal.
- Bearish Engulfing – A strong bearish reversal signal.
- Doji – Indicates market indecision.
- Hammer – Bullish reversal pattern after a downtrend.
- Shooting Star – Bearish reversal pattern after an uptrend.
5. Volume Analysis
Volume measures the strength of a price move.
5.1 High Volume Signals
- Uptrend with high volume → Strong bullish move.
- Downtrend with high volume → Strong bearish move.
- Breakout with high volume → Confirmation of trend continuation.
5.2 Low Volume Signals
- Uptrend with low volume → Weak rally, potential reversal.
- Downtrend with low volume → Weak sell-off, potential bounce.
6. Risk Management & Trading Strategy
6.1 Setting Stop-Loss & Take-Profit
- Stop-Loss – Protects against major losses.
- Take-Profit – Ensures gains are locked in before reversals.
Common risk-reward ratio: 1:2 or 1:3 (risking $100 to gain $200 or $300).
6.2 Position Sizing
- Never risk more than 1-2% of total capital on a single trade.
- Diversify holdings to reduce risk exposure.
6.3 Trading Psychology
- Avoid FOMO (Fear of Missing Out).
- Control emotions and stick to a strategy.
- Use a trading journal to improve decision-making.
7. Combining Technical & Fundamental Analysis
While technical analysis helps predict short-term price movements, fundamental analysis provides insight into a project’s long-term value.
Key fundamental factors to consider:
- Project team & partnerships
- Roadmap & adoption rate
- Tokenomics & supply structure
- On-chain data (whale activity, transaction volume)
7.1 Best Approach: Hybrid Strategy
- Use TA for trade timing.
- Use FA for long-term investment selection.
Conclusion
Technical analysis is a vital skill for crypto traders, allowing them to make informed trading decisions. Mastering trends, indicators, patterns, and volume will help you identify profitable opportunities while managing risks effectively.
Start practicing by analyzing Bitcoin or altcoins on TradingView and refining your TA skills!


