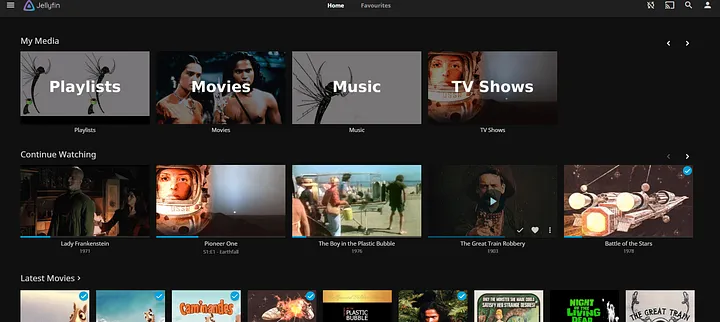
Jellyfin is a free, open-source media server that allows you to organize, manage, and stream digital media across multiple devices. It is a great alternative to Plex and Emby, offering full control without requiring a subscription.
This guide will walk you through installing Jellyfin on Ubuntu, setting up media drive permissions, configuring a reverse proxy with Apache or Nginx, and securing it with a Let’s Encrypt SSL certificate.
Step 1: Update Your System
Before installing Jellyfin, update your system to ensure all existing packages are up to date. Run the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Step 2: Install Dependencies
Install required packages for Jellyfin by running:
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates gnupg2 curl git -y
Step 3: Install Jellyfin Media Server
Jellyfin is not available in Ubuntu’s default repositories, so you need to add the official repository.
To import the GPG key for package verification, run:
wget -O – https://repo.jellyfin.org/jellyfin_team.gpg.key | sudo apt-key add –
Next, add the Jellyfin repository by executing:
echo “deb [arch=$( dpkg –print-architecture )] https://repo.jellyfin.org/ubuntu latest main” | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jellyfin.list
Now, update the package list to recognize the new repository:
sudo apt update
Finally, install Jellyfin:
sudo apt install jellyfin
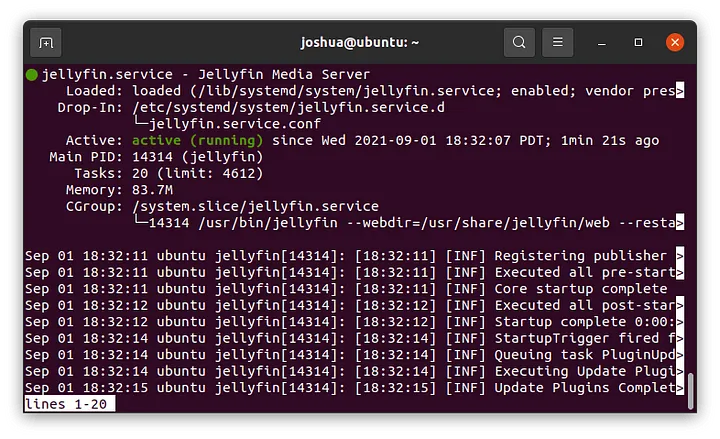
After installation, check if the Jellyfin service is running by executing:
systemctl status jellyfin
If it is not running, start and enable it using the following commands:
sudo systemctl start jellyfin
sudo systemctl enable jellyfin
Step 4: Access the Jellyfin Web Interface
Once Jellyfin is installed, open your web browser and go to the following address:
Follow the setup wizard to configure Jellyfin:
- Select your language and click Next.
- Create an admin username and password, then click Next.
- Add media libraries by selecting folders with your movies, TV shows, or music.
- Choose metadata language and click Next.
- Configure remote access settings and click Next.
- Click Finish to complete the setup.
Once logged in, you will see your Jellyfin dashboard with all configured media libraries.
Step 5: Configure Media Drive Permissions
Jellyfin requires read and execute permissions on media directories. Instead of using chown or chgrp, use the setfacl command.
First, install the ACL package by running:
sudo apt install acl -y
Then, grant Jellyfin access to media folders by executing:
sudo setfacl -R -m u:jellyfin:rx /media/mymediadrive
If you want to apply permissions to a specific directory or file, use this command:
sudo setfacl -m u:jellyfin:rx /media/mymediadrive/specific-folder
Step 6: Set Up a Reverse Proxy
To access Jellyfin remotely, you can configure a reverse proxy using Apache or Nginx.
Option 1: Apache Reverse Proxy
Install Apache by running:
sudo apt install apache2 -y
Enable necessary modules with the following command:
sudo a2enmod proxy proxy_http headers proxy_wstunnel
Create a new Apache configuration file by executing:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/jellyfin.conf
In the editor, add the following configuration, replacing DOMAIN_NAME with your actual domain:
VirtualHost *:80
ServerName DOMAIN_NAME
ProxyPreserveHost On
ProxyPass “/socket” “ws://127.0.0.1:8096/socket”
ProxyPassReverse “/socket” “ws://127.0.0.1:8096/socket”
ProxyPass “/” “http://127.0.0.1:8096/“
ProxyPassReverse “/” “http://127.0.0.1:8096/“
/VirtualHost
Save the file, then enable the configuration and restart Apache by running:
sudo a2ensite jellyfin.conf
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Option 2: Nginx Reverse Proxy
Install Nginx by running:
sudo apt install nginx -y
Create a new Nginx configuration file by executing:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/jellyfin.conf
In the editor, add the following configuration, replacing DOMAIN_NAME with your actual domain:
server {
listen 80;
server_name DOMAIN_NAME;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8096;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_buffering off;
}
}
Save the file, then test and reload Nginx by running:
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl reload nginx
Step 7: Secure Jellyfin with an SSL Certificate
To enable HTTPS for your Jellyfin server, use Let’s Encrypt SSL with Certbot.
First, install Certbot.
For Apache, run:
sudo apt install python3-certbot-apache -y
For Nginx, execute:
sudo apt install python3-certbot-nginx -y
Now, generate an SSL certificate.
For Apache, run:
sudo certbot –apache –agree-tos –redirect –hsts –staple-ocsp –email you@example.com -d DOMAIN_NAME
For Nginx, execute:
sudo certbot –nginx –agree-tos –redirect –hsts –staple-ocsp –email you@example.com -d DOMAIN_NAME
After completing the setup, Jellyfin will be accessible via HTTPS at:
Step 8: Updating Jellyfin
To update Jellyfin, run the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
Step 9: Uninstall Jellyfin (If Needed)
To remove Jellyfin, run:
sudo apt remove –purge jellyfin -y
To delete the repository, execute:
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jellyfin.list
Conclusion
You have successfully installed Jellyfin Media Server on Ubuntu. Now, you can stream media across multiple devices, set up a reverse proxy for external access, and secure it with SSL encryption.
Would you like help with optimizing performance, adding transcoding support, or integrating Jellyfin with cloud storage? Let me know! ?


